electron affinity chart|electron affinity table values : iloilo The electron affinity ( EA) of an element E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy . Cheltenham Festival Tips for Day 4 Races 2025. The final day of the week but the big one headlined by the Blue Riband of the National Hunt season, the Cheltenham Gold Cup which will be the centrepiece of the Cheltenham Festival day 4. Juvenile hurdlers kick off the day in the Triumph Hurdle, a race which saw Willie Mullins’ Majborough win the .
PH0 · why does electron affinity decrease down
PH1 · how to tell electron affinity
PH2 · how to calculate electron affinity
PH3 · greatest electron affinity
PH4 · electron affinity trend periodic table
PH5 · electron affinity table values
PH6 · electron affinity on periodic table
PH7 · arrange these elements according to electron affinity
PH8 · Iba pa
Fluffy In Space Jackpot is a Jackpot version of Fluffy in Space. This super cute slot developed by Eyecon features 5-reels and 25 paylines. . The only thing differentiates each title is the RTP, theme and the availability of the .
electron affinity chart*******Ago 11, 2023 Unlike electronegativity, electron affinity is a quantitative measurement of the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gas atom. The .Electron affinity can be defined in two equivalent ways. First, as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom. The second (reverse) definition is that electron affinity is the energy required to remove an electron from a singly charged gaseous negative ion. The latter can be regarded as the ionization energy of the –1 ion or the zeroth ionization energy. Either convention can be used. CALCULLA - Table of electron affinity of elements. Table shows electron .The electron affinity ( EA) of an element E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy .
The electron affinity ( Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state .Learn what electron affinity is, how it differs from electronegativity and ionization energy, and how it varies across the periodic table. See a chart of electron affinity values and factors that influence them.Electron affinity refers to the energy released when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom to form a singly charged negative ion. Alternatively, it can also be defined as the energy required to detach an .What is Electron Affinity. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. It is the opposite of ionization energy [1-4]. How to Find Electron Affinity. .electron affinity chartWhat is Electron Affinity. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. It is the opposite of ionization energy [1-4]. How to Find Electron Affinity. . Electron affinity ( Eea) is the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gas phase. In simple terms, it is a measure of a neutral atom’s .The electron affinity is the potential energy change of the atom when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form a negative ion. So the more negative the electron affinity the more favourable the electron .The chemical equation for electron affinity is as follows [1-4]. X (g) + e – → X – (g) When an electron approaches a neutral atom, the positively charged nucleus attracts it. The atom transforms into a negatively .
The electronic affinity is amount of energy, that is released during the attachment of the electron to the neutral atom. As a result of such attachment, a negative ion (anion) is formed. Electron affinity is related to electronegativity of elements.Simply speaking, the greater the affinity of electrons, the more eagerly the atoms of a given element join .Electron affinity is the attraction a neutral atom has for a non-bonding electron. Moving from left to right and bottom to top on the period table, electron affinity increases. This is because going from left to right and bottom to top, the atomic radius decreases so it is easier for the nucleus to attract negative electrons.

Electron Affinities of the Main-Group Elements* The electron affinity is a measure of the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. For example, when a neutral chlorine atom in the gaseous form picks up an electron to form a Cl- ion, it releases an energy of 349 kJ/mol or 3.6 eV/atom.The electron affinity is somewhat the opposite of ionization energy; however, it is not the reverse process. Remember, in ionization, we remove an electron from an atom forming a cation, while here, the electron is added to the atom forming an anion. If they were reverse processes, then the absorbed and released energies would have had the same . The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (1.1.2.4.1) (1.1.2.4.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is . Electron Affinity. In most cases, the formation of an anion by the addition of an electron to a neutral atom releases energy. This can be shown for the chloride ion formation below: Cl +e− → Cl− + energy Cl + e − → Cl − + energy. The energy change that occurs when a neutral atom gains an electron is called its electron affinity.
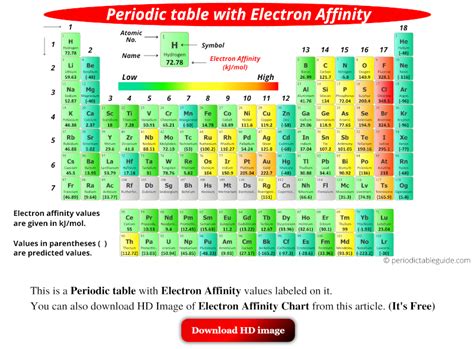
Electron affinity chart for all the elements of periodic table is shown in the below table. These values are in kJ/mol and the values written in parentheses ( ) are the predicted values. Atomic number Elements Electron affinity (kJ/mol) 1: Electron affinity of Hydrogen (H) 72.78: 2: Chart of Periodic Table Trends. Use this chart to see at a glance the periodic table trends of electronegativity , ionization energy , atomic radius , metallic character, and electron affinity. Elements are .electron affinity table valuesA7: Electron Affinities. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion. X(g) +e− → X−(g) + energy (A7.1) (A7.1) X ( g) + e − → X ( g) − + e n e r g y.electron affinity chart electron affinity table valuesA7: Electron Affinities. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion. X(g) +e− → X−(g) + energy (A7.1) (A7.1) X ( g) + e − → X ( g) − + e n e r g y. The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (4.5.1) (4.5.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is .
Electron affinity is the energy change that results from adding an electron to a gaseous atom. For example, when a fluorine atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form F⁻(g), the .THe electron affinity is the nergy required to detach an electron from the singly charged negative ion (energy for the process X -> X + e). The equivalent more common definition is the energy released (E initial + E final) when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule.[IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (Gold Book), 2nd .The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (2.8.1) (2.8.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is required . The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity for an added electron) are those with the smallest size and highest ionization energies and are located in the upper right .
We define the first electron affinity as the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous electrons are added to 1 mole of the element to form 1 mole of gaseous negative ions. First electron affinities are typically negative values. This is because when an electron is added to a neutral atom, energy is released in an exothermic process.
How To Use Our NFL Scores To Handicap Football Games. Our NFL scores and schedule page displays final NFL betting results from recent NFL games and informs bettors which totals and moneylines were accurate, as well as Sportsbook and closing spreads. Odds Shark’s NFL scores page also shows predicted NFL results, instant handicapping for .
electron affinity chart|electron affinity table values